From Dima: Melinda, you signed up for a summer internship project that will take a lot of your time and effort. This will not be easy. Please set your expectations that there will be a lot of work to do. Your parents will probably be checking this page and keep bothering you on “why you didn’t update this page for 2-3-4-5… days now?” Remember, all you will get from this is a piece of paper that will state that you passed (or failed) summer internship at biotechnology company in Austin, TX.
Please use this page as your science notebook for your summer internship – all your answers, observations, questions, and results – all should be added here on this page (you can add text and post pictures here; using this page will also teach you how to use the WordPress platform). I will be adding comments here as well. Please feel free to call me anytime at 512-350-0302 (if I don’t answer the phone just type your comments here and I will respond back on this page).
Please start with internet research regarding the instrument you received by answering the following questions (copy/paste will not work, you will need to perform the internet research using google.com and then write your own answers to the following questions):
Model and name of the instrument: Labomed CXL Monocular Microscope
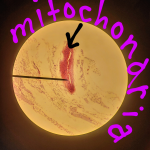
What is it used for? To study small objects such as tissues, cells , and mitcondria.
Who needs it?
What parts is it made of? Stand,Eyepiece,Nosepiece,Objectives,Mechanical Stage,Condenser.
How does it work? Describe in great detail.
Were you able to find an instrument manual online? Yes
Read the manual. Describe what was clear in the manual and what was confusing. It was clear in the manual how to turn on the microscope and how to make the microscope to focus on the sample. It was confusing to understand how the microscope works.
Read the details on what is Histology, how H&E works, how to identify different type of cells and tissue (how different disease cells/tissues look?):
A Beginner’s Guide to Haematoxylin and Eosin Staining
https://histology.leeds.ac.uk/what-is-histology/H_and_E.php
After you have completed internet research, try to turn on the instrument and see what happens. Make a picture and post it here. You may be missing power cord and/or adapter cables (find out what cords/cables/adapters are missing, find missing part on Amazon or Ebay, and post Amazon/Ebay link here, so I can get you the missing part). Some instruments been in storage and are very dusty – clean them with Windex spray and paper towels (your parents got a cleaning supplies cabinet somewhere in your house, find it).
Try to operate the instrument using the manual … is it working? Do you need certain supplies to make it work? Find the catalog numbers (from the manual) of the required supplies, where from they are available and post here links of what we need to order. Post here results of your testing, and how do you plan to move forward.
This is your notebook now … write and post answers and pictures below:
Melinda: This is how it looks when I turned on the microscope. I didn’t know how to make it focus on an object so I decided to find a manual on the internet to learn how to use the microscope properly.

Melinda: Me looking through the microscope

So far I got to get the microscope to focus by following the directions of the manual. The manual really helped me figure out how to use the microscope properly by following all the directions given me step by step. Down below are the pictures I got by taking a picture from the phone. So far so good!
Melinda: I plan to move forward by every day studying different samples that I have and to also compare them from other samples by writing notes. Also, I really don’t know yet how to figure out what each part of the cell is called but I will figure that out.
Me studying a sample
Melinda: This is the video I found to learn how to set up the microscope and to make it work.
Melinda: I also found this video to help me identify cells neutrophil series. I have also been trying to answer questions that I do have through Google.

Melinda: This is the sample that I am studying right now.
I have also noticed that the difference between animal cells and plant cells:
Animal cells:
Smaller
- Have no cell wall
- Have a nucleus in the center
- Have many vacuoles
- Cannot synthesis nutrients
- No plasmodesmata
Plant Cells:
Larger
- Has a cell wall
- Nucleus on the side
- One Vacuole
- Synthesizes Nutrients
- Has Plasmodesmata
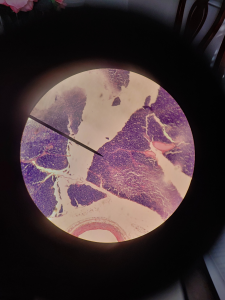
The big whitish open areas of the tissue are called the adipose tissue. This tissue also has fats ( which are the purple dots in the adipose tissue ) which are called the nuclei. Another major feature of the adipose tissue would be the cytoplasmic membrane which is the strands that are connected to the nuclei which form the adipose cells.
FUN FACT: Adipose tissue can comprise cell containing fat and oil.
Adipose tissue video

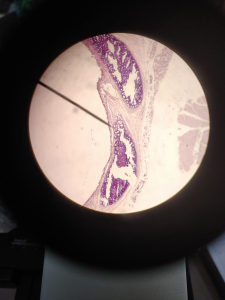
The picture above is a picture of Fibrocartilage through a microscope. The fibers in Fibrocartilage are dense like hairs. The nuclei in Fibrocartilage are in little clusters/lines. The purple dots in the Fibrocartilage is called chondrocytes which is the nuclei in the tissue.
FUN FACT: Fibrocartilage is made up of ground substance and chondrocytes.

This is a video that I found about Fibrocartilage.
CELLS:
- Are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism
- Main purpose of a cell is to organize
Examples: Blood cells , Muscle cells , Fat cells , etc.
FUN FACT ABOUT CELLS: Cells are made up of proteins and organelles
TISSUES:
- Capable of performing the simple task
- If there is some damage in the tissue it can be repaired by fibrosis
Examples: Nerve tissue, Muscles tissue, Connective tissue, etc.
FUN FACT ABOUT TISSUES: Fat and muscle are types of tissue
ORGANS:
- Different organs work for different purposes
- Size is greater than a tissue
Examples: stomach, lungs, heart, brain,etc.
BOTH TISSUES AND ORGANS:
- Tissues and Organs are made up of cells
- Both are found in multicellular organisms


FUN FACT: Fibrocartilage is a very strong and tough tissue found at the insertions of ligaments and tendons.
FUNCTION:

FUNCTION: They give elastic cartilage great flexibililty and strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body like ears.
FUN FACT:Elastic Cartilage contains elastic fibers in addition to collagen 🙂
The elastic cartilage contains elastic fiber networks and collagen type II fibers. The principal protein is elastin. Another thing is that elastic cartilage is a type of cartilage present in the outer ear.
Here is a video I found on YouTube to help me figure out Elastic Cartilage:
FUN FACT: Your right lung is heavier than your left lung
FUNCTION: The lung tissue keeps you alive and healthy
- Inhalation and Exhalation
- External Respiration Exchanges Gases
- Internal Respiration Exchanges Gases
- Air Vibrating the vocal cords creates sound